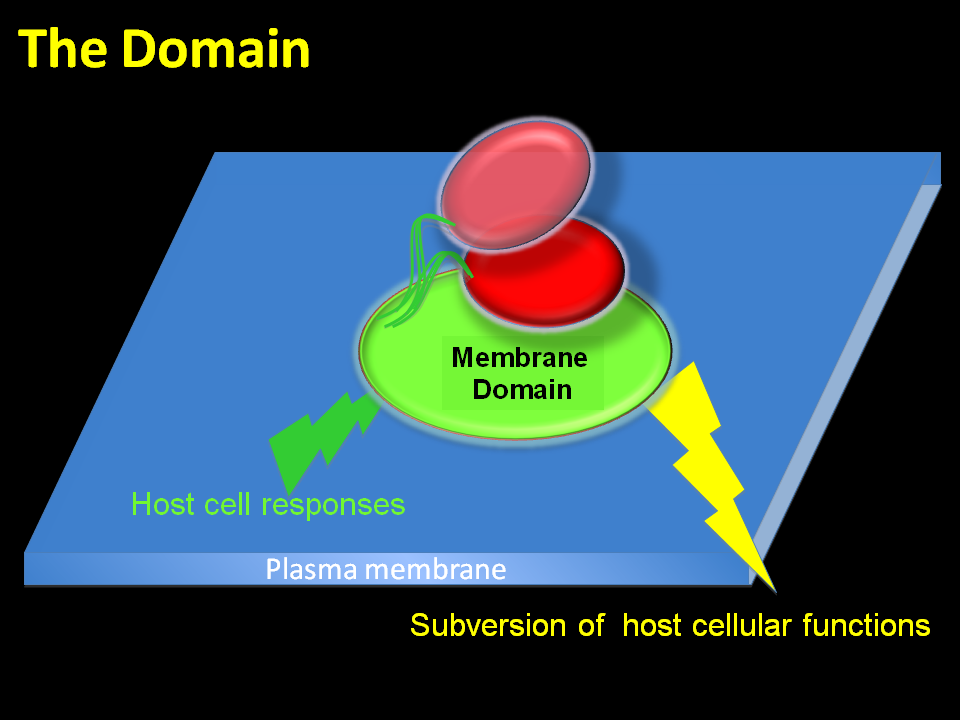
We hypothesize that upon contacting the apical plasma membrane, EPEC and EHEC generate a unique membrane domain, reminiscent of a lipid raft domain, at their attachment site to the plasma membrane. This bacteria-made membrane domain is enriched with distinct lipids and proteins that transmit harmful signals to the host cells. However, the host cell may respond by launching counteracting signals, such as innate immune danger signals, aimed at exterminating the domain and the pathogen. Therefore, studying the biochemical composition of this ‘pathogenic module’ is crucial for understanding the EPEC and EHEC diseases.
Open Questions:
• How do bacteria generate and modulate the membrane domain?
• What is the biochemical composition of the domain?
• Which host signaling pathways are hijacked by the domain, and how do they affect the pathogen and the host?
Our Contribution: PMID: 18987340; PMID: 30037792; PMID: 31242273

